| Pest | Description & Damage Caused |
|---|---|
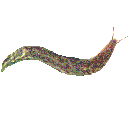 |
Slug Slugs are molluscs - snails without the shell - and are particularly fond of young seedlings. Slugs can be hunted out and killed individually, or you can take preventative measures. You can use slug pellets based on formalin, but use these with care as they are poisonous. Aluminium sulphate crystals kill the slugs by dehydrating them. You can make a beer slug trap and drown them. |
 |
Snail Snails are the same as slugs, but more decorative and easier to pick up. You are more likely to get snails in places with limestone or chalk soils, as they need the calcium to build their shells. As well as demolishing small seedlings, they also munch holes in leaves. Snails are dealt with in the same way as slugs. |
 |
Millepede Millipedes are round, black, heavy-looking insect-like animals about an inch long that you find under pots curled up like a spiral of wire. They have two pairs of legs on each segment, unlike centipedes, which only have one pair. Millipedes feed on decaying or soft vegetation, so can attack young seedlings, but they are not usually a problem. |
 |
Centipede Centipedes are brown, flat animals about an inch long with one pair of longish legs on each segment, and usually run away when you discover them hiding under pots. They are mostly carnivorous, and eat other pests such as slugs, so they are generally beneficial in the garden. |
 |
Earwig Earwigs are small thin brown animals with long antennae at the front and two long pincers at the back. They can damage plant buds and flowers, especially multi-petalled flowers like Chrysanthemum and Dahlia. They also eat small insects like aphids, so can be beneficial. Earwigs can be trapped in upturned pots filled with straw, or plants may be sprayed with systemic insecticide. |
 |
Woodlouse The Woodlouse is a crustacean, with a greyish or brownish body about half an inch long divided into segments. Some species roll into a ball when disturbed. Woodlice live in damp places and feed mainly on decaying vegetation, so are generally beneficial to the gardener, although they sometimes attack seedlings. They can be caught and removed, or chemical control can be used if really necessary. |
 |
Caterpillar Caterpillars are the larvae of butterflies, moths and other winged insects. Their sole function is to eat plants until they are big enough to turn into adults. Caterpillars eat holes around the edges of leaves, but are not usually interested in small seedlings. Caterpillars usually occur singly or in small numbers, so can be removed individually (and put in another part of the garden to complete their life-cycle if you like). |
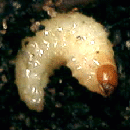 |
Vine Weevil Larva Vine Weevils are flightless beetles with long noses which lay their eggs in soil, particularly in pots of plants and seedlings. The larvae are about half an inch long, fat and white with brown heads but no legs. They eat the roots of plants, and often the first you know about it is when your plants are dead. The grubs are resistant to many insecticides, but you can use a soil drench, or biological control (nematodes which transmit a fatal bacteria), or you can pick them out of your pots by hand. |
 |
Cranefly Craneflies are rather elegant, long-legged insects that emerge in late summer from eggs laid the previous year. The female can lay up to 300 eggs, usually just below the surface, often in lawns but also in garden soil. The Craneflies themselves cause no damage to plants, except when they emerge and leave their larval cases embedded in lawns. Damage may also be caused by birds looking for the larvae. |
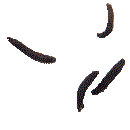 |
Leatherjacket These are the larvae of the Cranefly, and are dark brown tough-skinned grubs around an inch long, living just below the soil surface. They can cause damage to the roots and other underground parts of plants, particularly grasses in lawns. Leatherjackets can be encouraged to come to the surface by watering the area and covering it with dark polythene. They can then be collected and disposed of. |
 |
Fungus Gnat, Sciarid Fly One of the most troublesome pests in greenhouses, although it is mainly a nuisance to gardeners rather than a danger to plants. The Fungus Gnat is a small fly, breeding rapidly in warm conditions in leafmould, compost heaps and peat compost. The small larvae may damage plant roots. Fungus gnats can be dealt with by using sticky traps or an insecticide. |
 |
Springtail Springtails are tiny insects that are often present in large numbers in pots, but may not be noticed until the plants are watered, when they jump all over the surface using their forked tails. They can damage the leaves, stems and roots of seedlings. Springtails can be dealt with by using an appropriate insecticide on the soil surface. |